Pseudonymization vs. Anonymization: The Ultimate Privacy Showdown!
👉 Balancing privacy and utility
👋 Hello, Pharma Leaders!
A warm welcome to our 132 new subscribers! You've just joined the fast lane of Pharma industry insights. Buckle up – it's going to be an exciting ride!
Today, we're peeling back the layers on a hot topic that's often misunderstood but crucial in our data-driven world: data privacy.
Ever wondered about the difference between pseudonymization and anonymization? Confused about when to use which method? You're not alone!
We're about to demystify these concepts and show you how they can make or break your data strategy.
In this article, we'll explore:
🖇️ The key differences between pseudonymization and anonymization
🔎 When and why to choose one over the other
📊 The implications for your data management and research
📌 Real-world applications in the pharma industry
Whether you're a seasoned data guru or just dipping your toes into the world of health data privacy, this article will equip you with the knowledge to navigate this key topic with confidence. Ready to become a data privacy pro? Let's dive in!
In an era where data is often called the new oil, the healthcare industry finds itself sitting on a goldmine of information.
Patient records, clinical trials, and medical research generate vast amounts of data that could potentially revolutionize healthcare.
However, with great power comes great responsibility, especially when it comes to protecting patient privacy.
This is where the concepts of pseudonymization and anonymization come into play, offering different approaches to safeguarding sensitive health information while still allowing for its valuable use.
Understanding the Basics
Before diving into the nuances, let's establish a clear understanding of these two data protection methods:
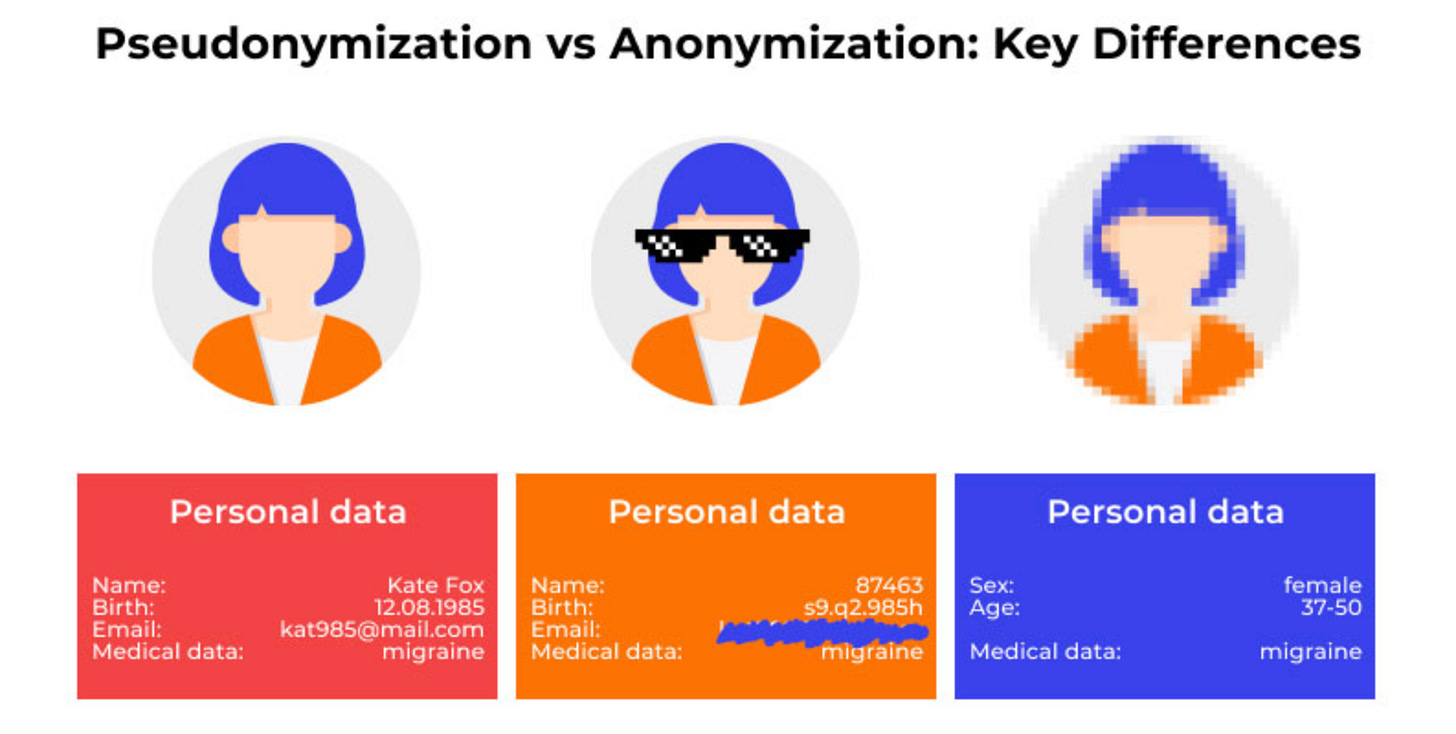
Pseudonymization
Pseudonymization is a data management technique that replaces personally identifiable information (PII) with artificial identifiers or pseudonyms. The original identifiers are kept separately and securely, allowing for the possibility of re-identification under specific circumstances.
Anonymization
Anonymization, on the other hand, is the process of irreversibly removing or altering all personal identifiers from data, making it impossible to re-identify individuals from the dataset.
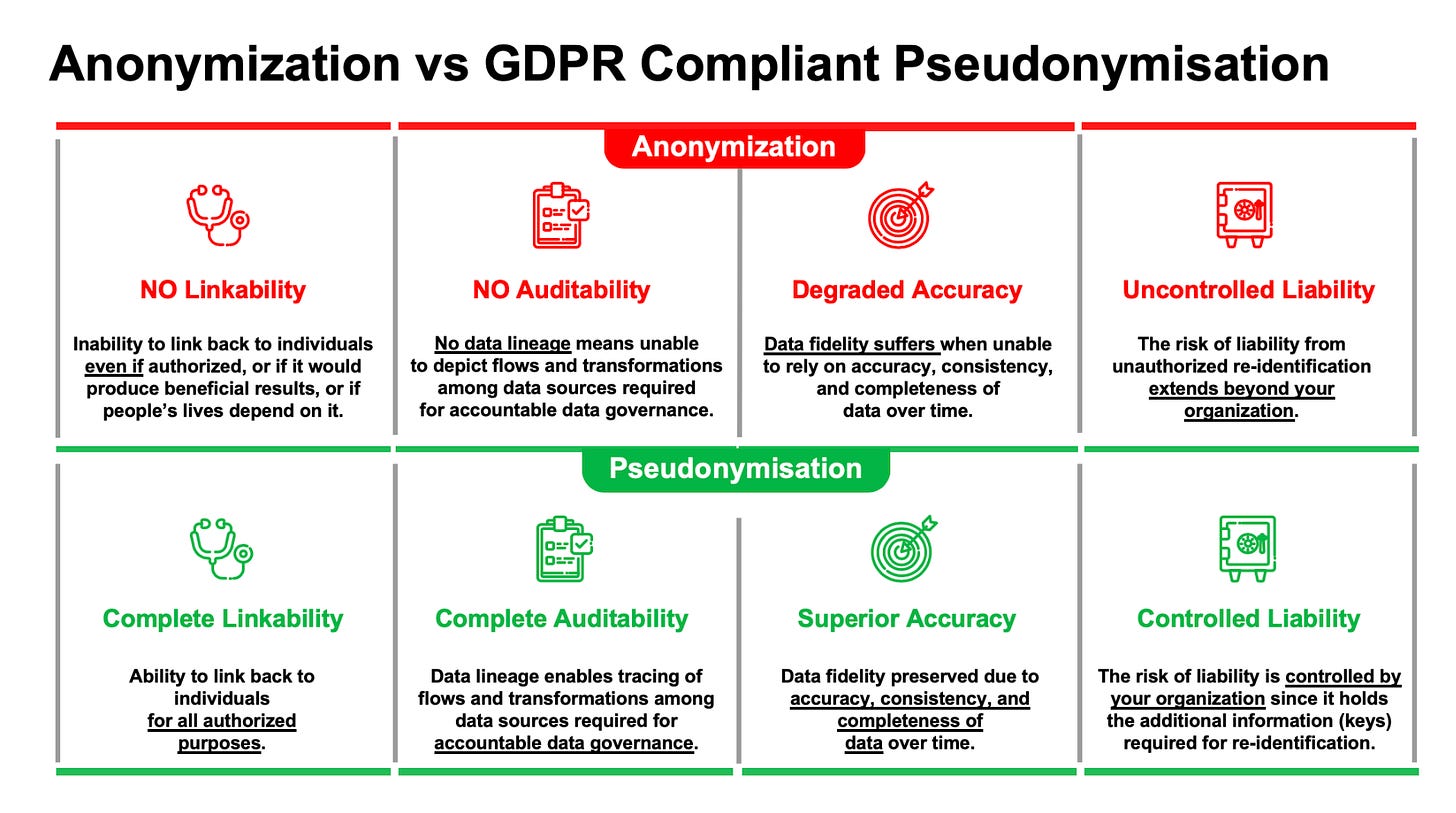
The Key Differences
While both methods aim to protect individual privacy, they differ significantly in their approach and implications:
Reversibility:
Pseudonymized data can be reversed to identify individuals if necessary.
Anonymized data is permanently altered, making re-identification impossible.
Data Utility:
Pseudonymization maintains data integrity and allows for more detailed analysis.
Anonymization may reduce data utility due to the permanent removal of identifiers.
Legal Status:
Pseudonymized data is still considered personal data under regulations like GDPR.
Anonymized data is generally not considered personal data under most regulations.
Use Cases:
Pseudonymization is often preferred in clinical settings where linking patient data over time is crucial.
Anonymization is more suitable for general statistical analysis or public data releases.
Pseudonymization in Practice
Imagine a hospital system that wants to conduct a longitudinal study on diabetes management.
Using pseudonymization, they could replace patient names and social security numbers with unique codes.
This allows researchers to track individual patient progress over time without knowing their identities.
If a critical health issue arises, authorized personnel can use the secure key to re-identify the patient and provide necessary care.
Anonymization in Action
Consider a public health department releasing data on COVID-19 cases.
They might anonymize the data by removing names, exact addresses, and dates of birth.
Instead, they could provide age ranges, general location data (e.g., zip codes), and other non-identifying information.
This allows for valuable public health analysis while protecting individual privacy.
The Pros and Cons
Pseudonymization
Pros:
Maintains data utility and allows for detailed analysis
Enables data linking across records and time
Allows for re-identification when medically necessary
Cons:
Requires robust security measures to protect the re-identification key
Still considered personal data, subject to stricter regulations including patient consent
Potential for re-identification if the key is compromised
Anonymization
Pros:
Provides stronger privacy protection
Reduces regulatory burden as it's not considered personal data
Allows for broader data sharing and public release
Cons:
Reduces data utility and granularity
Prevents individual-level analysis and data linking
Irreversible process, limiting future use cases
Choosing the Right Approach
The choice between pseudonymization and anonymization depends on various factors:
Intended Use: If the data needs to be linked or analyzed at an individual level over time, pseudonymization is often the better choice.
Regulatory Environment: In highly regulated industries, anonymization might be preferred to reduce compliance burdens.
Risk Tolerance: Organizations with lower risk tolerance might opt for anonymization to minimize the chance of data breaches.
Data Value: If the data's value lies in individual-level insights, pseudonymization preserves more of this value.
As technology evolves, so do the methods of data protection.
Advanced techniques like differential privacy are emerging, offering new ways to balance data utility and privacy.
However, pseudonymization and anonymization remain fundamental tools in the data protection toolkit.
Challenges & Considerations
In the complex world of health data management, there's no one-size-fits-all solution.
Pseudonymization offers a balance between privacy and utility, making it valuable for many healthcare applications.
Anonymization provides maximum privacy but at the cost of reduced data usability.
As the healthcare industry continues to harness the power of big data, understanding these approaches is crucial for everyone from policymakers to healthcare providers.
Ultimately, the goal is to unlock the potential of health data while respecting and protecting individual privacy.
By carefully considering the strengths and limitations of pseudonymization and anonymization, we can work towards a future where data drives medical breakthroughs without compromising patient trust.
If you want more and to keep in touch 👋



Even though pseudonymization and anonymization are helpful models in ensuring Data security and protection of patient’s privacy, however it still fall short in meeting all researchers needs. I hope these models developed further in the age of AI so it’s easier to implement and conduct research. Great post .